Open Source Data: Urbanization-led Land Cover Change Impacts Terrestrial Carbon Storage Capacity in Pakistan (1990–2020)
Overview
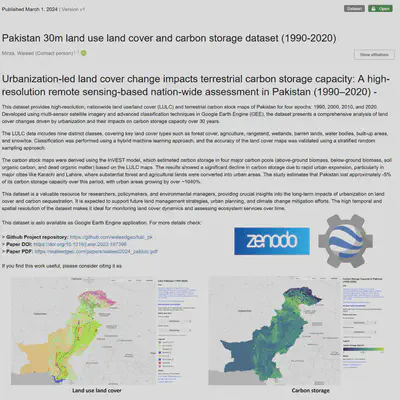
I am pleased to announce that our study, “Urbanization-led land cover change impacts terrestrial carbon storage capacity: A high-resolution remote sensing-based nationwide assessment in Pakistan (1990–2020)”, has been published in Environmental Impact Assessment Review.
Dataset Availability
We have open-sourced our comprehensive Pakistan 30m Land Use Land Cover (LULC) and Carbon Storage Dataset (1990–2020), covering four time periods: 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020. This dataset provides valuable insights into land cover transformations and carbon storage dynamics over the past three decades in Pakistan.
- Zenodo Archive: Access the dataset on Zenodo
- Google Earth Engine Assets: See Earth Engine Access for direct use within the GEE platform.
Citation
If you find this work useful, please consider citing our paper:
@article{waleed2024_paklulc,
title={Urbanization-led land cover change impacts terrestrial carbon storage capacity: A high-resolution remote sensing-based nationwide assessment in Pakistan (1990–2020)},
author={Waleed, Mirza and Sajjad, Muhammad and Shazil, Muhammad Shareef},
journal={Environmental Impact Assessment Review},
volume={105},
pages={107396},
year={2024},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
- Paper DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2023.107396
- Download PDF: Download the full paper
Dataset Description
Our dataset offers high-resolution, nationwide Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) and terrestrial carbon stock maps of Pakistan for the years 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020. Utilizing multi-sensor satellite imagery and advanced classification techniques within Google Earth Engine (GEE), this dataset enables detailed analysis of land cover changes due to urbanization and their impacts on carbon storage over 30 years.
Key Features
- Spatial Resolution: 30 meters
- Temporal Coverage: 1990, 2000, 2010, 2020
- LULC Classes: Nine distinct land cover types
- Carbon Pools: Above-ground biomass, below-ground biomass, soil organic carbon, and dead organic matter
- Methodology: Hybrid random forest-based machine learning approach with approximately 40,000 stratified random samples for training and validation
- Applications: Urban planning, climate change mitigation, environmental management, policy-making
Key Findings
- Urban Expansion: Urban areas in Pakistan expanded by over 1040% between 1990 and 2020.
- Carbon Storage Loss: There was an approximate 5% decrease in terrestrial carbon storage capacity over the study period.
- Regional Variations:
- Major cities like Karachi and Lahore experienced moderate urban sprawl.
- Emerging cities such as Rawalpindi and Peshawar underwent rapid expansion.
- Land Conversion: Significant shifts from rangelands (~47%) and agricultural lands (~35%) to built-up areas.
- Afforestation Efforts: Positive impacts in northern regions, but significant north-south disparities in carbon loss.
Earth Engine Access
The datasets are also available as Earth Engine assets for direct use within the GEE platform.
Earth Engine Snippets
// LULC Images
var lulc1990 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/lulc_pk/img1990');
var lulc2000 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/lulc_pk/img2000');
var lulc2010 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/lulc_pk/img2010');
var lulc2020 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/lulc_pk/img2020');
// Carbon Stock Images (values multiplied by 10 for scaling)
var carbon1990 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/carbon_pk/img1990').multiply(10);
var carbon2000 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/carbon_pk/img2000').multiply(10);
var carbon2010 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/carbon_pk/img2010').multiply(10);
var carbon2020 = ee.Image('projects/pak-var/assets/carbon_pk/img2020').multiply(10);
- Sample Code: Access sample code in Earth Engine Code Editor
Note
This dataset is included in the Awesome GEE Community Catalogue.
Web Applications
Interactive Google Earth Engine (GEE) applications are available to explore the datasets:
Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Viewer
- Access the App: Pakistan LULC Viewer (1990–2020)
- Features:
- Select province and district
- Visualize LULC for 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020
Carbon Storage Viewer
- Access the App: Pakistan Carbon Storage Viewer (1990–2020)
- Features:
- Select province and district
- Visualize carbon storage for 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020
Contact
For any queries or collaboration opportunities, please contact:
- Mirza Waleed
- Email: waleedgeo@outlook.com
- LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/waleedgeo
- Website: waleedgeo.com
Additional Resources
- Research Projects and Opportunities: UrbES Lab
- Contributors:
License
This project is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Note: To bulk download these datasets, please visit our Zenodo Archive.
